How the EU's New GDPR Regulations May Affect Your Business

Heralded as the most important change in data privacy regulation to hit the European Union in decades, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is set to take effect in the EU on May 25th. Meaning any organization that collects or processes personal data on citizens anywhere in the European Union will be required to meet new compliance regulations designed to protect consumer rights.
The new regulations are certainly welcome news for consumers worldwide, as the implications of GDPR span much further than the borders of the EU. The new rules, requiring organizations to provide more transparency to individuals regarding what and how their data is being used, is making end-users happy, but can be a bit frustrating for businesses, particularly because the international effects of the law change are still a bit of an unknown.
What has quickly become clear is that these regulations are far-reaching - they impact all facets of a business’ contact with consumers. Websites that use cookies, apps, email marketing or other touchpoints, such as event registrations or contests, where there is a possibility that the personal data of any EU or UK citizen may be collected are subject to GDPR and its associated penalties. We’re seeing websites scramble to get out pop-up alerts, terms of service changes, and even emails to notify users of the updated policies.
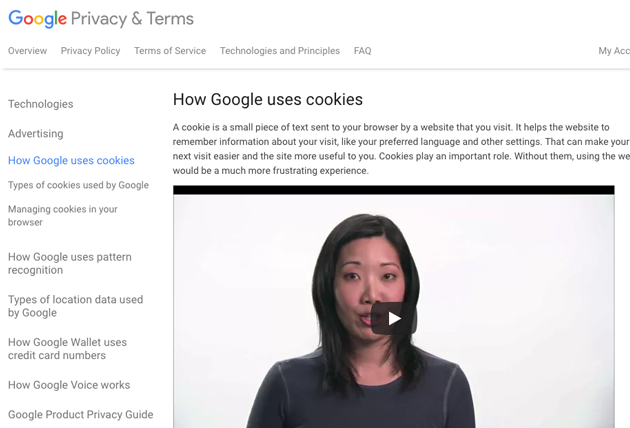
Google's "See Details" selection page, complete with a video explaining how their site uses cookies, and what a user can expect from consenting to use of their private data.
These regulations promote the idea of “Privacy by Default,” calling for all digital systems to be designed in a manner where privacy settings are automatically set to their highest level, later giving users the option to downgrade the severity of their privacy settings; generally, the opposite of how most privacy settings currently work.
Given the importance of these requirements, and the significance that it could have on data protection regulations for the foreseeable future, it is only natural for businesses to be concerned not only about how it affects them, but also how they plan to implement the necessary policy and procedural changes within their organization.
Here, we will be outlining steps to help make sense of these daunting new regulations and ensure a clear path to GDPR compliance for your business.
What Are GDPR Compliance Requirements?
While the implications may be more than a little ambiguous, GDPR compliance requirements can be broken down into a very strict and explicit set of rules and regulations organizations worldwide that deal in the EU must follow or be subject to a fine of €20 million or 4% of annual turnover.
The following are requirements that must be met starting May 25th according to GDPR standards:
- Provable Consent – All users, or data subjects, must provide “provable consent” before a data collector can process personal information.
- User Permission – Organizations must get permission from data subjects (individuals from whom data is collected) before collecting any personal information or adding them to any email marketing lists. However, it is important to note that submitting a form on a landing page, submitting an inquiry or signing up for a newsletter does NOT automatically constitute verifiable permission on behalf of the user.
- Full Disclosure – Data controllers (organizations that process personal data) must issue a full disclosure of what data is being collected/processed, for what purpose and how long the data will be stored. This also includes the contact information for all parties who manage/process the user data that is collected.
- User Opt-Out – All users have the opportunity to withdraw their previously-issued consent at any point.
- Data Breach Procedure – Organizations must define and maintain a response and disclosure process in the event of a data breach. Furthermore, if a data breach occurs, data controllers are required to notify the supervisory authority of the breach within 72 hours of becoming aware of the attack.
- Data Protection Officers – All data controllers are required to appoint a Data Protection Officer responsible for monitoring compliance of GDPR within the organization.
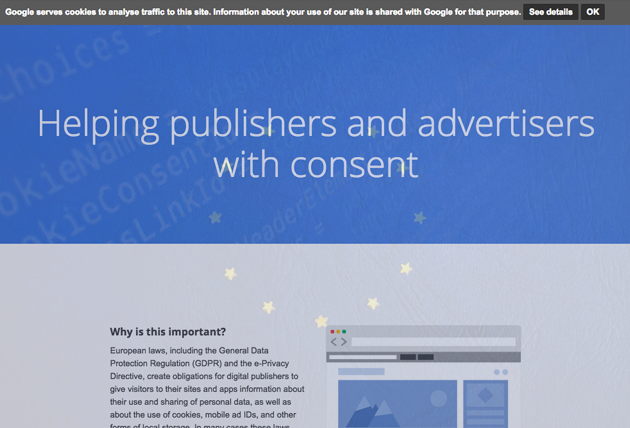
The grey topline bar shown here is an example of a user opt-in on Google's www.cookiechoice.org, a resource on privacy consent for the GDPR & e-Privacy Directive.
Recommendations Regarding Website Compliance
The following guidelines were developed with website compliance in mind, but the far-reaching implications of the GDPR also point to the need for similar steps to be taken with respect to internal data collection and storage procedures, as well as the collection and processing of data that might be captured from other activities (e.g., digital outreach, email, etc.)
These procedures and best practices can help ensure your website meets GDPR compliance requirements, and can be used as a framework for total compliance within your organization:
- Ensure your privacy statement is clear, accurate and prominently displayed on your homepage, and that it completely discloses what data is being collected, how it is being used, and how long it is stored. Additionally, it is recommended that you include contact information where questions or withdrawal of consent can be directed, should users have any concerns in the future.
- Expand the options for agreement of your privacy policy to easily allow users to opt-out. Instead of only allowing a user to agree to privacy terms, include both an “I agree” and an “I do not agree” button alongside the privacy statement that must be submitted by the user.
- Create a set of protocols for complying with requests by consumers to withdraw consent in a timely manner and be able to provide verifiable proof of the accommodation of these requests.
- Include affirmation of consent for anything that requires a personal data submission that may not meet all the disclosure regulations of GDPR such as newsletters, landing page forms or inquiries.
- Implement a process to ensure compliance with pseudonymized data provisions. This process involves transforming data in such a way that stops it from being attributed to a data subject without the inclusion of additional information.
- Ensure all third-party data processors (hosting, marketing platforms, CRMs, etc.) are GDPR compliant.
- Conduct a personal data audit to identify all first- and third-party data processors, along with how your organization is handling this information.
The introduction of GDPR is going to change the way users’ personal data is handled all over the world. While the impact of these new regulations on a global scale is still uncertain, following the procedures outlined above will help ensure GDPR compliance within your organization, while also improving the protection of user data, mitigating the impact of data breaches, and improving transparency between the organization and the user.
If you have any questions about GDPR, or if you would like Herrmann to assist with making your website GDPR compliant, please reach out to our chief business development officer, John Albert, at john@herrmann.com.


